Read the Brochure
Middleware: The Critical Step
A Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tracking system is much more than RFID hardware. For example, an often overlooked but critical need is middleware or software. Middleware communicates with interrogators and your backend systems.
First, it processes and filters tag data. Then, the data passes to your ERP or business system. Without software you’re just reading tag data, not utilizing it.
Benefits of Radley RFID
Radley’s RFID tracking system goes far beyond basic reporting tools. It’s designed to summarize and analyze your data. As a result, your end users, processes and operations see a valuable return on your investment.
- Boost Accuracy & Efficiency
- Reduce Inventory Time
- Real-Time Data & Metrics
- Advanced Security
- Reduce Material Expenses
- Meet Compliance Requirements
Best in Class Hardware
Middleware Bridges the Gap
Fully Configurable
Our flexible RFID tracking system integrates to almost any ERP. Also, it shapes to your existing processes and your specific workflow.
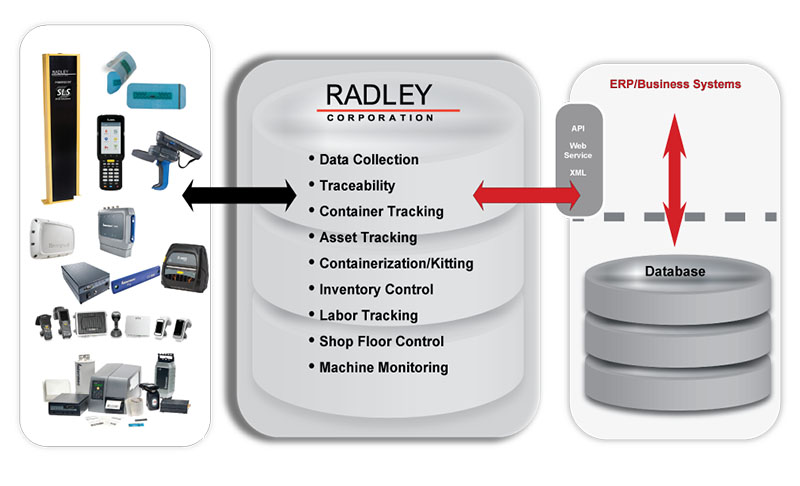
End-to-End Solution
From consulting, to software. to hardware selection, Radley gives you a total, end-to-end RFID solution.
- Software / Middleware
- Integration to ERP
- Consulting
- RFID Engineering
- Hardware, Tags & Labels
- Implementation & Training
- Support
RFID Technology and its Applications
RFID is a tracking solution that employs intelligent bar codes to track objects. The acronym stands for Radio Frequency Identification. The automatic technology uses electromagnetic fields or radio waves. These fields identify and track information stored in tags attached to items.
Unlike other data capturing methods, RFID can read tagged items from a reading distance of 3 to 300 feet away. Also, unlike the use of barcode readers, they do not have to be within the reader’s direct line-of-sight. Plus, RFID readers can read multiple tags simultaneously.
RFID - Transformative Technology
An RFID (radio frequency identification) system consists of three parts:
1. A scanning device (RFID reader, also called an interrogator)
2. A transceiver (RFID antenna) which interprets the data
3. A transponder (RFID tag) that contains programmed information
The scanning antenna emits radio-frequency signals. In turn, these signals provide the tag with a means of communicating.
There are two types of RFID tags: Active and Passive. Active RFID tags contain a battery and automatically broadcast their signal. An active RFID tracking system costs more than passive tags.
In contrast, “passive” RFID tags do not contain their own power source (batteries). In that case, the tags send information upon receiving RF energy emitted from a reader. Then, the scanning antenna picks up the information.
Besides the active and passive RFID tag distinction, RFID frequencies can vary as well. RFID frequency refers to the size of the radio waves within the system. Namely, there are low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF), and ultra-high frequency (UHF) waves.
In turn, each wave frequency behaves differently. As a result, each frequency has advantages and disadvantages.
For example, an RFID software system operating at a lower frequency may have a slower data read rate. But it is better able to read near ranges or on metal or liquid surfaces.
In contrast, a system operating at a higher frequency has faster read rates. Also, it is able to read tags from further away.
But, RFID at these frequencies is more sensitive to interference. This can be caused by liquids and metals in the environment.
RFID readers and tags are just part of a total RFID solution. Without software, or “middleware”, you can collect data, but it won’t be possible to use or analyze it.
RFID has many advantages over bar code technology or other optical readers. For one, it quickly identifies information stored on tags. The typical read time is less than 100 milliseconds.
Another advantage is RFID can read several tags at once rather than reading item by item. Similarly, barcode scanners must maintain a line-of-sight with each code. But with RFID the scanner only needs to be within read range of the tag to read it.
Also, RFID tags can be placed inside items, protecting them from wear. In comparison, barcodes must be on the surface of an object.
Radio Frequency Identification is becoming the technology of choice for modern industries. For example, industries that use RFID technology include automotive, pharmaceutical, and food processing. This is due to the growing need for automated labeling and traceability.
RFID WIP tracking is one area where manufacturers see immediate benefits. In this case, RFID adds real-time visibility to work in progress.
Also, the demand for mass production of goods continues to increase. With this, manufacturing companies are turning to RFID solutions to simplify logistics management.
For instance, inventory and supply chain management, counterfeit prevention and more see improvement. In inventory management, RFID is often combined with barcode labels to keep track of stock levels and location.
Also, RFID is a popular choice for a tool and asset tracking solution. An RFID Asset tracking system prevents loss and theft. At the same time, RFID keeps track of asset location of valuable devices, tools and equipment.
Finally, some firms are using RFID systems as a security measure. RFID tags on employee badges can provide access control to secure areas of a plant or office.
How Else Can Radley Help You?
Contact Us Today!
Talk to a Product Specialist to learn how Radley can help you.

